Germanium (Ge) is a robust, high-density optical material renowned for its excellent infrared (IR) transmission while effectively blocking ultraviolet (UV) and visible (VIS) light. It transmits efficiently from approximately 2 µm onward, making it a preferred material for mid-wave infrared (MWIR) and long-wave infrared (LWIR) applications. With the highest refractive index among commonly used IR-transmitting materials and relatively low optical dispersion, germanium enables compact, high-performance lens designs. To mitigate its inherently high surface reflectance, anti-reflective (AR) coatings are strongly recommended.
Infrared Transmission & Thermal Behavior
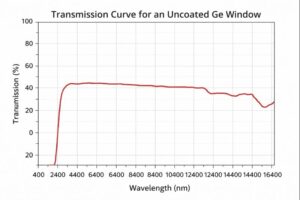
Uncoated germanium IR windows typically transmit >45% total IR light across the 2–14 µm range (depending on thickness). With AR coatings, transmission can be significantly increased within the target band.
Germanium exhibits temperature-dependent transmission behavior:
- Up to ~45°C: Stable IR transmission
- Around 100°C: Gradual increase in absorption
- Above ~200°C: Rapid degradation of transmission due to free-carrier absorption
For sustained high-temperature environments, germanium windows require thermal management or alternative materials. Additionally, germanium’s high density may be a consideration in weight-sensitive systems.
- Hardness: ~HK 780 (slightly higher than GaAs)
- Mechanical note: Strong yet brittle; appropriate mounting and handling are required
Optical Properties
- Transmission Range: ~2–14 µm (MWIR & LWIR)
- Refractive Index: ~4.0 at 10 µm, enabling fewer lens elements and compact designs
- Dispersion: Relatively low in the IR, helping reduce chromatic aberration
(Transmission curve for an uncoated Ge window depends on thickness; AR coatings substantially improve performance.)

Physical & Environmental Properties
- Density: ~5.323 g/cm³
- Thermal Conductivity: Moderate; suitable for systems with controlled thermal loads
- Thermal Expansion: ~6 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ (design consideration for temperature cycling)
- Hygroscopicity: Non-hygroscopic (does not absorb moisture)
- Spectral Limitation: Opaque in the visible spectrum; not suitable for VIS applications
Applications of Germanium IR Windows
- Thermal imaging systems (front optics)
- Military & defense optics (e.g., FLIR, night vision)
- FTIR spectroscopy and analytical instruments
- Satellite and aerospace IR imaging
- Industrial monitoring and inspection
Limitations
- Cost: Higher than many optical materials
- Temperature Sensitivity: Reduced transmission at elevated temperatures
- Weight: High density may affect system mass budgets
Shape Optics Germanium (Ge) Crystals Specifications
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 12mm ~ 380mm |
| Length | Customizable |
| Electrical Resistivity | 5 – 40 Ω·cm (optical grade) |
| Crystal Structure | Single Crystal / Polycrystalline |
| Crystal Purity | 99.999% ~ 99.99999% |
| Conduction Type | N-type / P-type |
| Surface Roughness | Ra max 0.2µm – 4.0µm |
| Refractive Index @ 10.6µm | 4.0052 |
| Absorptance @ 10.6µm | ≤0.035 |
Factory Standard
- Window sizes: 2 mm – 100 mm
- Diameter tolerance: +0 / −0.05 mm
- Thickness tolerance: +0.01 / −0.03 mm
- Flatness: 1/2 λ
- Parallelism: < 3 arc minutes
- Surface quality: 20-10 scratch-dig (no dig)
- Edge finish: Protective bevel
- Transmission: >47.5% @ 3.7–4.8 µm (uncoated)
(Higher transmission achievable with AR coatings or custom designs)
Contact us for manufacturing limits or custom specifications.
Germanium Solutions from Shape Optics
At Shape Optics, we offer a comprehensive range of Germanium IR windows, including AR- and DLC-coated options optimized for 7–12 µm, as well as custom germanium windows tailored to your specifications. Our portfolio also includes germanium lenses, prisms, and blanks, all manufactured and tested in our state-of-the-art metrology lab to meet stringent quality standards.
Contact us to discuss your application requirements, custom designs, or coating options.

