Fiber optical adapters are vital components in optical communication systems, ensuring efficient and reliable signal transmission. Common types include FC/PC Simplex Multimode adapters, LC/APC Simplex Single Mode connectors, and SC/UPC Simplex Single Mode connectors. But what do PC, APC, and UPC stand for, and how do they differ? This article delves into these terms and explains their significance, while also highlighting the role of shape optics engineering in enhancing fiber optic technologies.
Types of Fiber Connectors
- FC (Ferrule Connector)
- Description: FC adapters feature a threaded body for secure connections, ideal for high-vibration environments.
- Applications: Telecommunications, measurement instruments, and high-speed networks.
- Advantages: High precision and durability.
- PC (Physical Contact)
- Description: PC adapters have a spherical end-face that reduces air gaps and lowers Optical Return Loss (ORL).
- Applications: General fiber optic systems, including LANs and telecommunications.
- Advantages: Improved signal integrity with ORL values around <-35dB.
- UPC (Ultra-Physical Contact)
- Description: UPC adapters extend the polishing process of PC connectors for an even finer surface finish, further reducing back reflection.
- Applications: High-speed data transmission, digital video, and telecommunications.
- Advantages: Enhanced performance with ORL values around <-55dB.
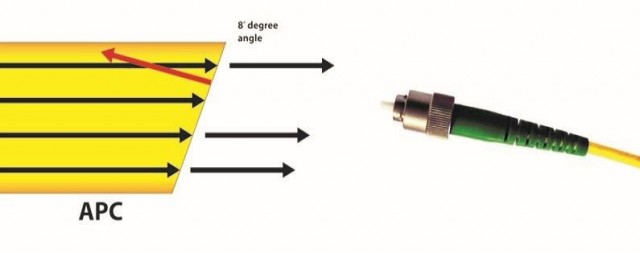
- APC (Angled Physical Contact)
- Description: APC adapters have an 8-degree angled end-face, reducing back reflection by directing light into the cladding.
- Applications: CATV, analog systems, and passive optical networks (PONs).
- Advantages: Superior ORL performance, around <-65dB, ideal for high-precision applications.
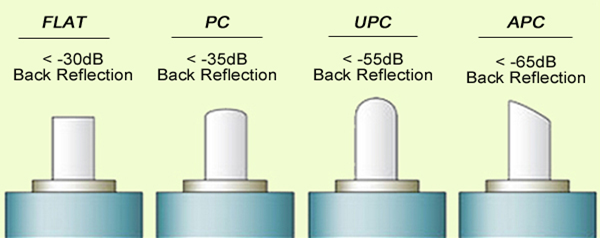
Optical Return Loss (ORL)
ORL is the reflection of light back to the source, which can harm the laser source and disrupt the transmission signal. Different connector types have varying ORL levels, affecting their performance and suitability for specific applications.
- Flat Fiber Connector: High ORL, not suitable for single-mode fibers.
- PC Connector: Reduced ORL compared to flat connectors, better performance.
- UPC Connector: Further reduced ORL, suitable for high-speed data and digital systems.
- APC Connector: Lowest ORL, ideal for precision applications.

Differences Between UPC and APC
UPC and APC connectors dominate the market, each with distinct characteristics:
- UPC Connectors: Polished with a slight curvature, reflecting light back to the source. ORL should be -55dB or greater.
- APC Connectors: Polished at an 8-degree angle, reflecting light into the cladding. ORL should be -65dB or greater.
APC connectors are preferred for applications requiring high precision and low back reflection, while UPC connectors are suitable for less sensitive digital systems.

Selecting the Right Fiber Connector
Choosing the right connector depends on the application’s requirements, including cost, simplicity, and optical performance. APC adapters are commonly used by cable companies and FTTX providers for their superior performance in high-precision signaling. UPC connectors, while less precise, are still widely used for their reliability in less demanding applications.


All these adapters have a place in the market, with APC being the preferred choice for high-precision applications and UPC for less sensitive systems. The selection should be based on specific needs and application requirements.
Our expertise in shape optics engineering drives innovation in fiber optic technology, providing custom solutions, cutting-edge research, and quality assurance. By leveraging our skills, we deliver superior optical performance and set industry benchmarks.
For more information on how our shape optics engineering can benefit your fiber optic applications, contact us today.
