
Cooled LWIR lenses can be differentiated by several key characteristics:

Cooled LWIR Lenses:
Uncooled LWIR Lenses:
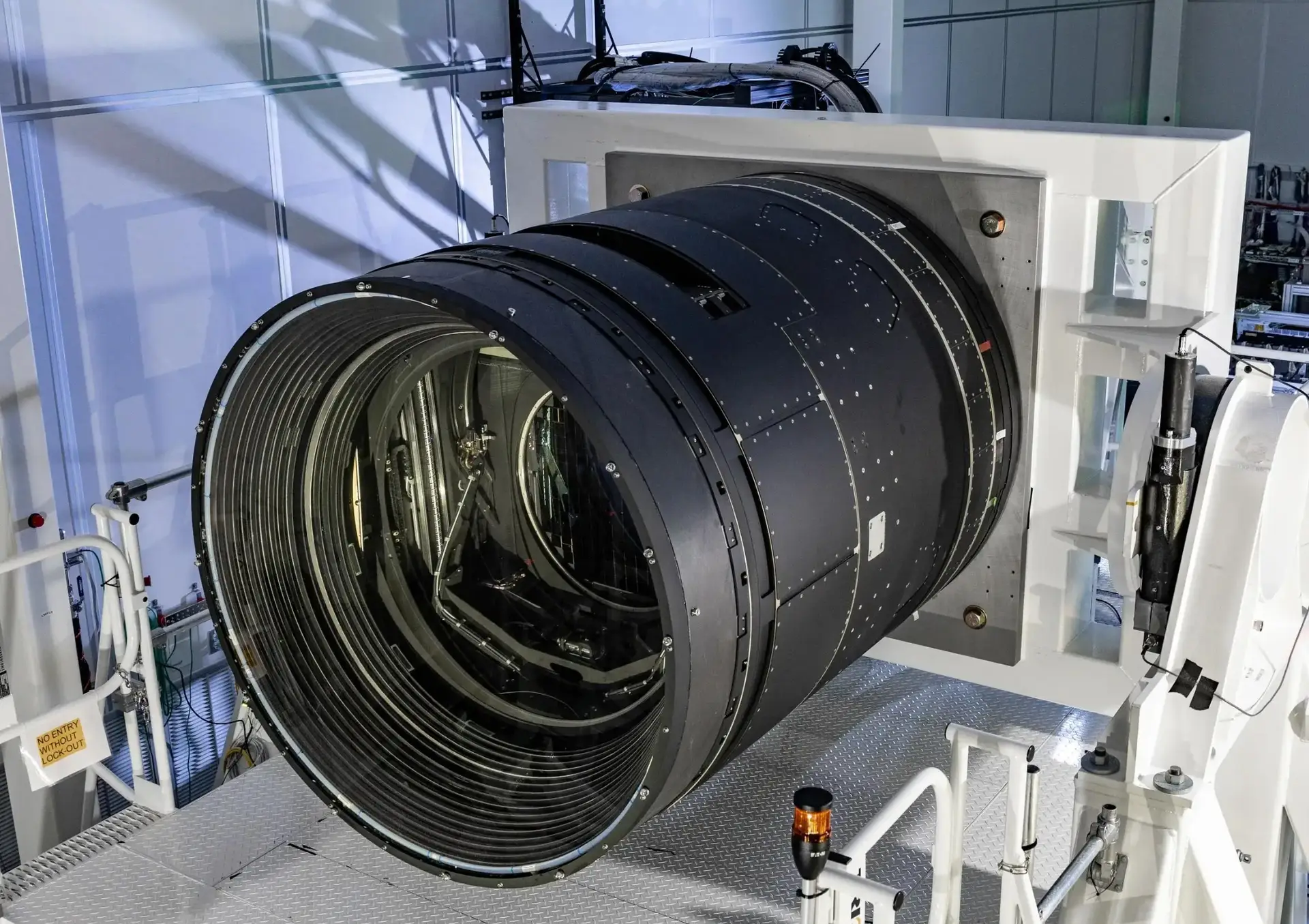

Cooled LWIR lenses are integral to advanced imaging systems that require precise, high-resolution thermal imaging across various professional and scientific applications. These systems are particularly valued in fields where the ability to detect slight differences in thermal signatures from a distance can be critical.
Shape Optics’ unwavering commitment to excellence propels the advancement of Infrared Optical (IR Optical) Modules. With Shape Optics, the unseen is revealed, and mysteries are deciphered. Enhance your innovation trajectory with Shape Optics’ Infrared Optical Module Solutions—redefining the limits of perception. Contact Shape Optics today to begin a transformative journey with our custom Infrared Optical (IR Optical) Module imaging solutions.