An aplanatic lens is a lens that is free of both spherical and coma aberrations, making it ideal for applications requiring high precision, such as laser beam delivery systems. In double-pass aplanatic optics, where light interacts with an optical element more than once, we need to model both the forward and reverse paths of the beam. While this process can be tedious and prone to errors, the Make Double Pass tool in OpticStudio offers an efficient solution.
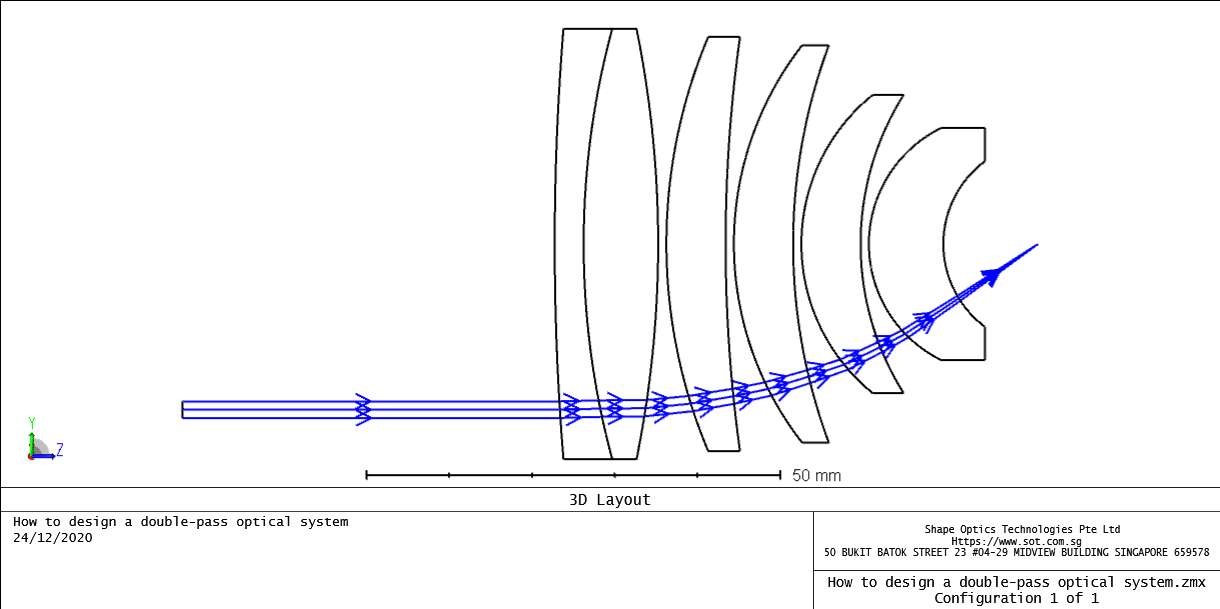
The initial input data is as below:

The “Make Double Pass tool” is a convenient way to replicate and reverse a sequential system in design a double-pass aplanatic laser beam delivery system.
It is found in the toolbar of the LDE: Lens Data Editor…Make Double Pass. Users need to specify the surface at which rays are to reflect.
The reflect surface is converted to a mirror, all surfaces prior to it are replicated in reverse after the mirror, and pickup solves are applied to all parameters (including lens and extra data values) to link the first and second pass surface data. Note that any nominal surfaces that come after the reflect surface will be deleted when using this tool.
Open the double-pass aplanatic optics laser beam delivery system sample file attached to this article. The file attached in the end of this article models an aplanatic laser beam delivery system with a decentered beam incident upon the optical system. It is to simulate a double pass system, whereby the beam reflects from the image plane and travels back through the optical components. 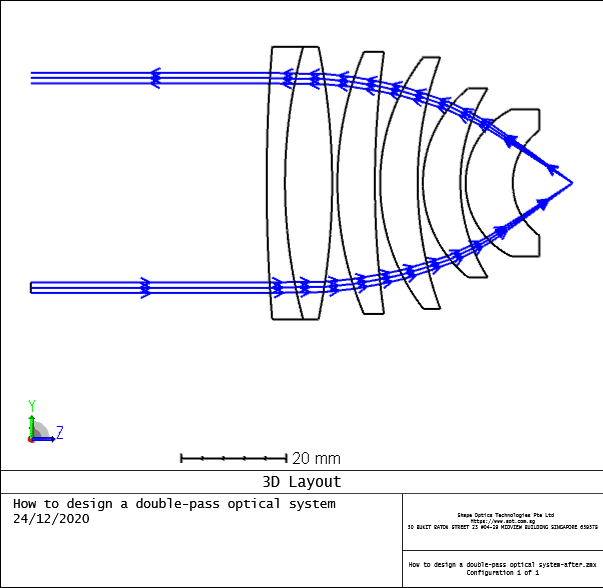
This can easily be done with the Make Double Pass tool. Open the tool and select surface 14 as the reflect surface.

After pressing OK, notice the layout updates to show the beam coming in through the bottom of the lenses, reflecting off surface 14, and exiting through the top of the lenses.
Reference
- Laikin, Milton. Lens Design. CRC Press, 2007.
- https://www.zemax.com/
- The design file used in this article is attached. How to design a double-pass aplanatic laser beam delivery system
