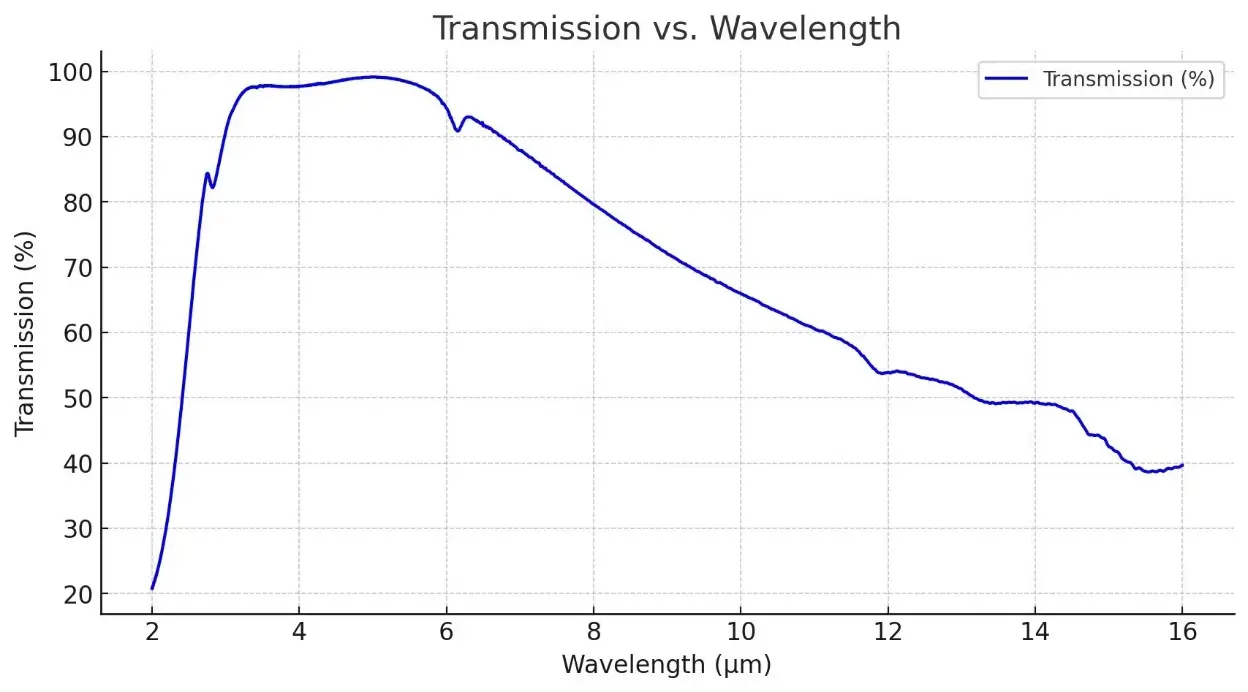
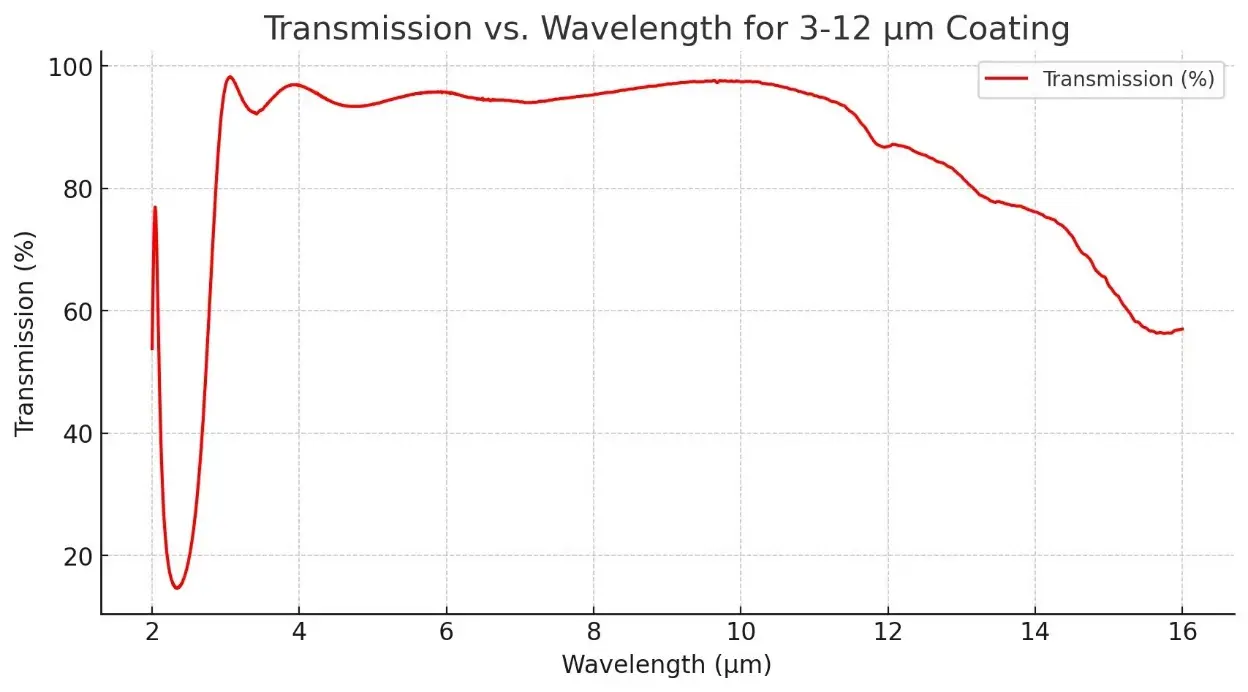
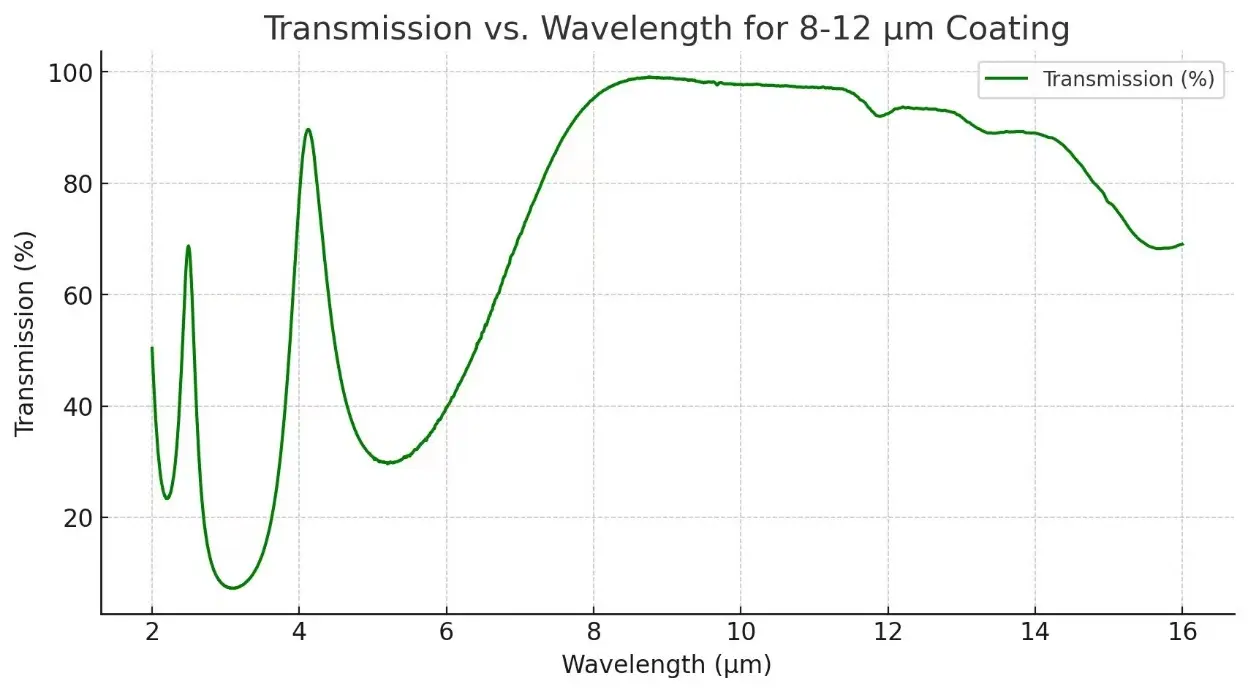
Description
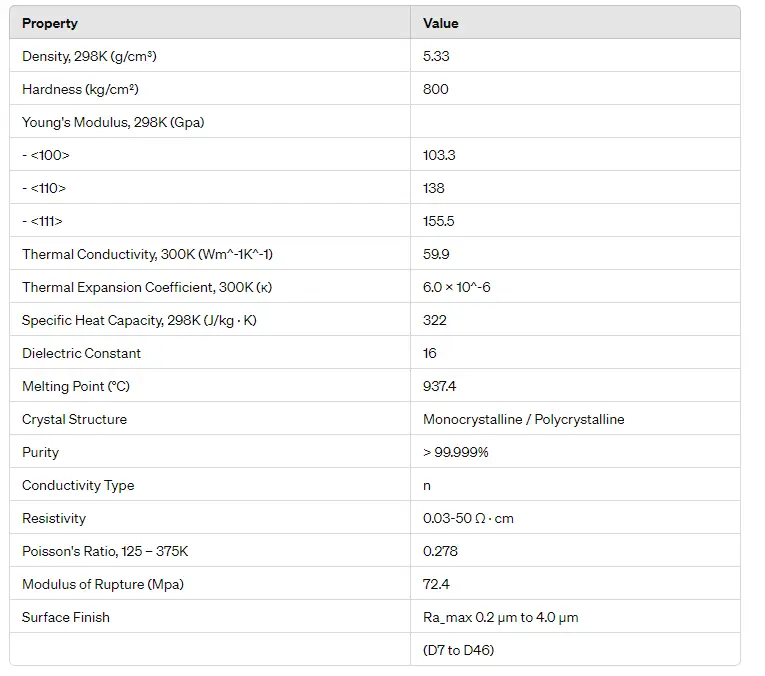
N-type germanium is a semiconductor material formed by doping germanium with donor impurities that introduce excess free electrons. These electrons become the majority charge carriers, significantly influencing the material’s electrical behavior.
Doping Elements
N-type germanium is typically doped with group V elements, such as:
- Phosphorus
- Arsenic
- Antimony
These dopants have five valence electrons, one more than germanium. The additional electron becomes weakly bound and is easily available for electrical conduction.
Electrical Properties
- Majority Charge Carriers: Electrons
- Electrical Conductivity: Increased compared to intrinsic germanium due to the higher free-electron concentration
- Carrier Motion: Under an applied electric field, electrons drift toward the positive terminal (anode)
- Conventional Current: Flows from positive to negative, opposite to electron motion
N-type germanium is known for its high electron mobility, which contributes to fast electrical response.
Uses in Technology
- Semiconductor Devices
-
- Transistors: N-type germanium is used in the manufacture of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Utilized in the production of various ICs due to its effective semiconductor properties.
- Infrared Detectors: N-type germanium is widely used as a substrate or functional material in certain IR detector technologies
- Optical and Infrared Applications
-
-
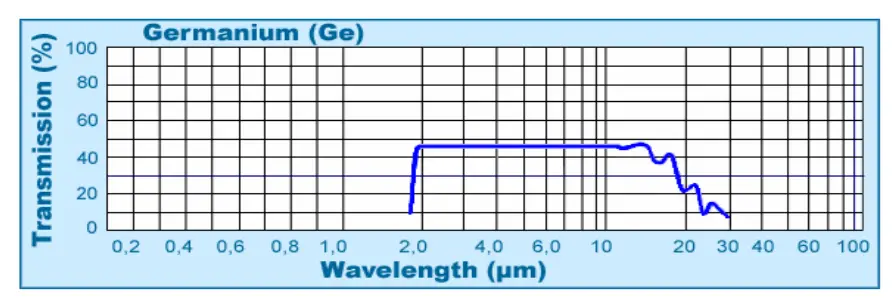
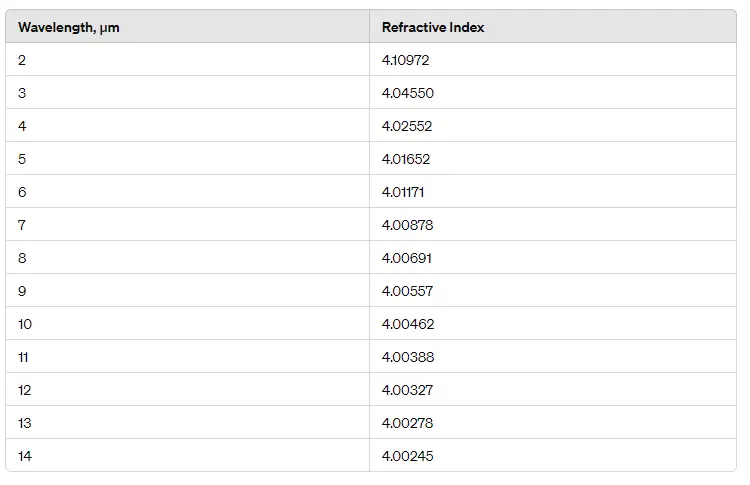
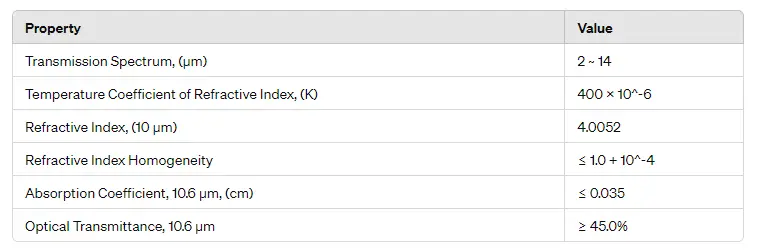
Infrared Optics: N-type germanium is commonly used as a substrate material for infrared lenses and windows due to its high refractive index and excellent IR transmission
-
Thin-Film Applications: Germanium can be used as a high-index layer in infrared optical coatings, though it is not itself an anti-reflective coating material
- Optical Storage Media: Germanium is not used as pure germanium layers in CDs, DVDs, or Blu-ray discs. Instead, these media use phase-change alloys (e.g., Ge–Sb–Te), where germanium is one component of a compound material
-
Advantages
- High Electron Mobility: Significantly higher than silicon, enabling faster device operation
- Infrared Compatibility: Excellent performance in IR optoelectronics and detector systems
- Material Versatility: Suitable for high-speed and high-frequency applications
Note: Due to its narrow bandgap, germanium is less suitable for high-temperature or high-power electronics compared to silicon.
Comparison to Silicon
- Similarities
-
- Both are group IV semiconductors
- Used in transistors, diodes, and integrated circuit technologies
- Can be doped to form N-type or P-type materials
- Differences
-
- Electron Mobility: Germanium > Silicon (improves speed)
- Bandgap: Germanium has a smaller bandgap, leading to higher leakage current
- Thermal Stability: Germanium has a lower melting point (~937°C) than silicon (~1414°C)
- Modern Usage: Silicon dominates mainstream electronics, while germanium is used in high-speed, infrared, and specialized applications
Summary
N-type germanium is an important semiconductor material characterized by high electron mobility and strong infrared compatibility. While it is no longer widely used in mainstream digital electronics, it remains highly valuable in infrared detectors, high-speed devices, optoelectronics, and IR optical systems. Its role in advanced semiconductor and optical technologies continues to be significant, particularly where speed and infrared performance are critical.