Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂) is a high-performance birefringent optical crystal widely used in VUV, deep-UV, visible, and infrared optical systems. With an exceptional transmission range from 110 nm to 7.5 μm, MgF₂ is one of the most reliable materials for demanding VUV and UV applications, particularly ArF excimer laser systems at 193 nm.
Its excellent chemical stability, high laser damage threshold, intrinsic birefringence, and resistance to thermal and mechanical shock make MgF₂ an industry-standard choice for precision windows, lenses, prisms, polarizers, and coating materials operating in harsh environments.
Optical Properties
-
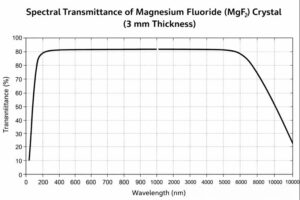
Ultra-Wide Transmission Range: 0.11 – 7.5 μm (VUV to mid-IR)
-
High Optical Transmittance: 90% from 193 nm to 6 μm (3 mm thickness, uncoated)
-
Low Reflection Loss: ~5.2% @ 0.6 μm (both surfaces, uncoated)
-
Intrinsic Birefringence: Ideal for UV polarizers, waveplates, and polarization-sensitive optics
-
Refractive Index (@ 0.7 μm)
-
nₒ = 1.37608
-
nₑ = 1.38771
-
-
Absorption Coefficient: 0.04 cm⁻¹ @ 2.7 μm
-
Thermo-Optic Coefficient (dn/dT)
-
2.3 × 10⁻⁶ /°C (‖ c-axis)
-
1.7 × 10⁻⁶ /°C (⊥ c-axis)
-
Physical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.18 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1255 °C |
| Crystal Structure | Tetragonal |
| Cleavage Plane | (110) |
| Molecular Weight | 62.32 |
Mechanical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Knoop Hardness | 415 kg/mm² (100 g indenter) |
| Young’s Modulus (E) | 138.5 GPa |
| Shear Modulus (G) | 54.66 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus (K) | 101.32 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.276 |
| Apparent Elastic Limit | 49.6 MPa (7200 psi) |
Thermal Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.3 W·m⁻¹·K⁻¹ @300 K |
| Thermal Expansion (‖ c-axis) | 13.7 × 10⁻⁶ /°C |
| Thermal Expansion (⊥ c-axis) | 8.9 × 10⁻⁶ /°C |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 1003 J·kg⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
Electrical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (‖ c-axis, 1 MHz) | 1.87 |
| Dielectric Constant (⊥ c-axis, 1 MHz) | 1.45 |
Chemical Stability
- Excellent resistance to most chemicals
- Extremely low water solubility: 0.0002g @ 20°C
- Suitable for vacuum, space, and long-term UV exposure
- Not recommended for prolonged exposure to strong acids
Typical Applications of MgF₂ Optics
- VUV & Deep-UV optics (ArF excimer laser windows at 193 nm, UV lithography, synchrotron optics)
- Laser optics (high-energy UV laser windows and low-absorption components)
- Astronomical & space optics (UV telescope windows, prisms, and low-scatter imaging optics)
- Optical coatings (vacuum evaporation material and UV–IR anti-reflection coatings)
Manufacturing Capabilities
| Parameter | Capability |
|---|---|
| Maximum Diameter | Ø170 mm |
| Clear Aperture | ≥ 85% |
| Surface Flatness | λ/4 @ 633 nm |
| Surface Quality | 20/10 scratch-dig |
Why Choose MgF₂ for VUV & UV Optical Systems?
Magnesium Fluoride remains the industry standard for deep-UV optics because it offers:
- Outstanding VUV transmission at 193 nm
- Excellent thermal and mechanical stability
- Low optical absorption and scatter
- Proven long-term reliability in laser, vacuum, and space environments
MgF₂ is also widely used as a UV polarizing material and as a vacuum-deposited coating material to enhance optical transmission across broad wavelength ranges.

